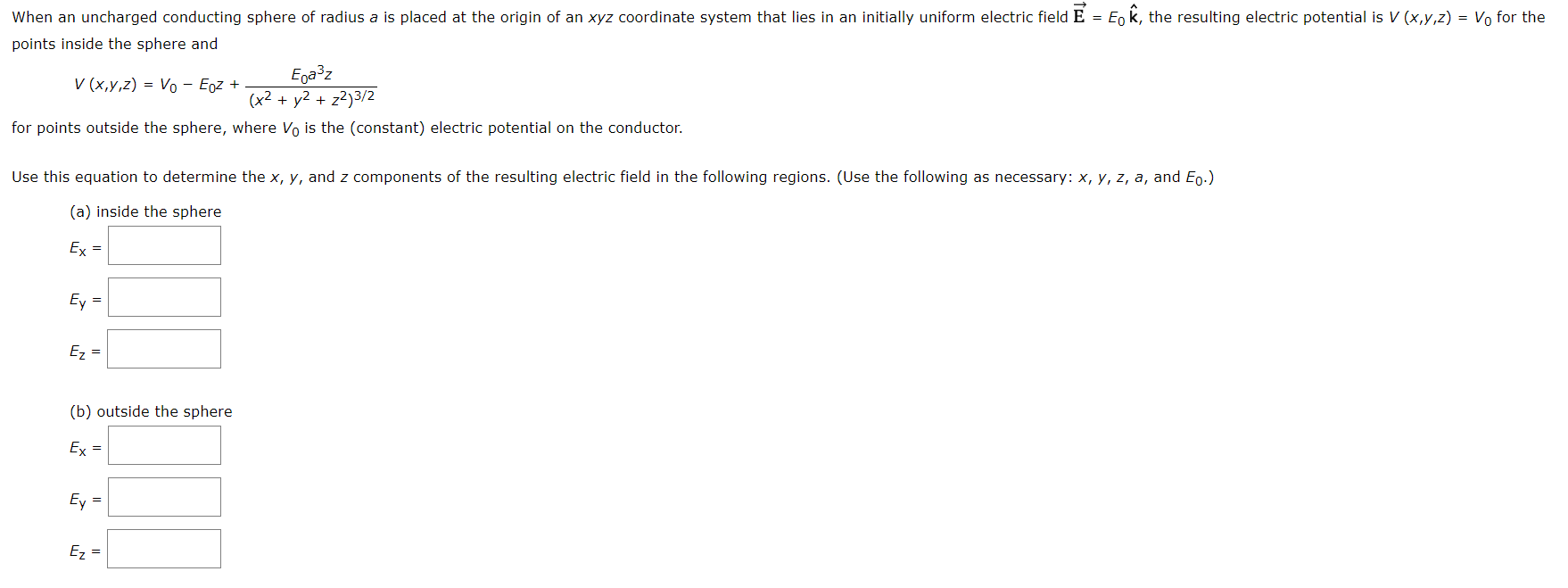
Z Resulting
A z-score equal to -1 represents an element, which is 1 standard deviation less than the mean; a z-score equal to -2 signifies 2 standard deviations less than the mean; etc. If the number of elements in the set is large, about 68% of the elements have a z-score between -1 and 1; about 95% have a z-score between -2 and 2 and about 99% have a z. Synonyms for resulting include consequential, ensuing, following, subsequent, collateral, consequent, resultant, subsequential, successive and accompanying. The semantic role of the noun phrase whose referent exists only by virtue of the activity denoted by the verb in the clause 1; a statement that solves a problem or explains how to solve the problem 1. He computed the result to four decimal places 1; something that results 1. He listened for the results on the radio 1; a phenomenon that follows and is caused by some previous phenomenon 1.
 -->
-->
Applies to: Windows Server (Semi-Annual Channel), Windows Server 2019, Windows Server 2016, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows Server 2012
Displays the Resultant Set of Policy (RSoP) information for a remote user and computer. To use RSoP reporting for remotely targeted computers through the firewall, you must have firewall rules that enable inbound network traffic on the ports.
Z Results
Syntax
Note
Except when using /?, you must include an output option, /r, /v, /z, /x, or /h.
Z Resulting
Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
/s <system> | Specifies the name or IP address of a remote computer. Don't use backslashes. The default is the local computer. |
/u <username> | Uses the credentials of the specified user to run the command. The default user is the user who is logged on to the computer that issues the command. |
/p [<password>] | Specifies the password of the user account that is provided in the /u parameter. If /p is omitted, gpresult prompts for the password. The /p parameter can't be used with /x or /h. |
/user [<targetdomain>]<targetuser>] | Specifies the remote user whose RSoP data is to be displayed. |
/scope {user computer} | Displays RSoP data for either the user or the computer. If /scope is omitted, gpresult displays RSoP data for both the user and the computer. |
[/x /h] <filename> | Saves the report in either XML (/x) or HTML (/h) format at the location and with the file name that is specified by the filename parameter. Can't be used with /u, /p, /r, /v, or /z. |
| /f | Forces gpresult to overwrite the file name that is specified in the /x or /h option. |
| /r | Displays RSoP summary data. |
| /v | Displays verbose policy information. This includes detailed settings that were applied with a precedence of 1. |
| /z | Displays all available information about Group Policy. This includes detailed settings that were applied with a precedence of 1 and higher. |
| /? | Displays help at the command prompt. |
Remarks
Group Policy is the primary administrative tool for defining and controlling how programs, network resources, and the operating system operate for users and computers in an organization. In an active directory environment, Group Policy is applied to users or computers based on their membership in sites, domains, or organizational units.
Because you can apply overlapping policy settings to any computer or user, the Group Policy feature generates a resulting set of policy settings when the user logs on. The gpresult command displays the resulting set of policy settings that were enforced on the computer for the specified user when the user logged on.
Because /v and /z produce a lot of information, it's useful to redirect output to a text file (for example,
gpresult/z >policy.txt).
Examples
To retrieve RSoP data for only the remote user, maindomhiropln with the password p@ssW23, who's on the computer srvmain, type:
To save all available information about Group Policy to a file named, policy.txt, for only the remote user maindomhiropln with the password p@ssW23, on the computer srvmain, type:
To display RSoP data for the logged on user, maindomhiropln with the password p@ssW23, for the computer srvmain, type:
Additional References

Home > How do I report Z-score data in APA style?
Background Enter Data Analyze Data Interpret Data Report DataThree thingsIt’s a good idea to report three main things in an APA style results section when it comes to z-scores. Doing so will help your reader more fully understand your results. 1. Test type and useYou want to tell your reader what type of analysis you conducted. You also want to tell your reader why this particular analysis was used. What did your analysis tests for? ExampleYou can report data from your own experiments by using the template below. “Z-scores were computed for raw scores in the ________ data set.” If we were reporting data for our example, we might write sentence like this. “Z-scores were computed for raw scores in the grades data set.” 2. The ValuesIt is most likely that you will want to tell your readers the values for a particular raw score and its’ corresponding z-score. You can report data from your own experiments by using the template below. “For the raw score ______, z = _____.” Just fill in the blanks by using the SPSS outputFill in the raw score and corresponding z-score. Once the blanks are full…You have a sentence that looks very scientific but was actually very simple to produce. “For the raw score 98%, z = 1.24.”3. Report your results in words that people can understandIt’s a good idea to report you results in an easy to understand language, after you have stated them scientifically. Imagine that you were trying to explain these results to a family member or friend who does not know much about science. ExampleYou might write something like this for our example. “This z-score tells us that my exam score was above the class average.” All together nowWhen you put the three main components together, results look something like this. “Z-scores were computed for raw scores in the grades data set. For the raw score 98%, z = 1.24. This z-score tells us that my exam score was above the class average.” Background Enter Data Analyze Data Interpret Data Report Data |