Occasional Quick Sharp Chest Pain
- Occasional Quick Sharp Chest Pains
- Sharp Chest Pain Center
- Occasional Quick Sharp Chest Pain Radiating
- Occasional Quick Sharp Chest Pain
Medically reviewed by: Marilyn Folk, BScN.
Last updated: December 12, 2020
Electric shock like feeling in the chest can be momentary discomfort in the chest, which causes sudden, sharp pain. Such sharp pains in chest are often rapid and last for few seconds to minutes. “While many different disorders can cause anterior front neck pain, neck pain associated with difficulty breathing, chest pain, feeling flushed or sweating, or palpitations should raise suspicion for acute. The most common heart problems that cause chest pain include: pericarditis – which usually causes a sudden, sharp, stabbing pain that gets worse when you breathe deeply or lie down angina or a heart.
Sometimes chest pain feels crushing or burning. In certain cases, the pain travels up the neck, into the jaw, and then radiates to the back or down one or both arms. Many different problems can cause chest pain. The most life-threatening causes involve the heart or lungs. You may worry that chest pain is due to a heart attack, which occurs when blood flow to the heart is blocked, typically by a blood clot and narrowed arteries. Classic symptoms include pressure or squeezing in the chest, lightheadedness, and pain in the shoulder, arm, neck, jaw, or back. To continue reading this article, you must log in.
Shooting chest pains anxiety symptoms description:
You experience:
- Shooting pains in the chest.
- A sudden sharp, stabbing, and/or shooting pains in the chest and/or heart area.
- A pressure in the chest.
- A fullness in the chest area.
- Stabbing pains so strong they take your breath away.
- Shooting pains that start in the chest and radiate to the back, shoulders, neck, head, or face.
- A feeling like someone is stabbing you in the chest or heart.
These shooting pains chest symptoms can also present in a wide variety and/or combinations, such as just shooting pains or just pressures, as well as a combination of stabbing pains and pressures. They don’t necessarily have to occur as one or the other, but can also occur as a combination of pains and pressures.
Anxiety shooting chest pains can persistently affect one area of the chest only, can shift and affect another area or areas of the chest, and can migrate all over the chest, and can affect many areas of the chest over and over again.
Anxiety shooting chest pains can come and go rarely, occur frequently, or persist indefinitely. For example, you may feel shooting chest pains once in a while and not that often, feel them off and on, or feel shooting chest pains all the time.
Anxiety shooting chest pains may precede, accompany, or follow an escalation of other anxiety sensations and symptoms, or occur by itself.
Anxiety shooting chest pains can precede, accompany, or follow an episode of nervousness, anxiety, fear, and elevated stress, or occur ‘out of the blue’ and for no apparent reason.
Anxiety shooting chest pains can range in intensity from slight, to moderate, to severe. They can also come in waves, where the shooting chest pains are intense one moment and ease off the next.
Anxiety shooting chest pains can occur intensely for a moment or two, then disappear the next.
Anxiety shooting chest pains can persist for a few days, then completely disappear. Or they can persist indefinitely no matter what you do.
Anxiety shooting chest pains can change from day to day, and/or from moment to moment.
All of the above combinations and variations are common.
Advertisement - Article Continues Below
What causes anxiety shooting chest pains?
When shooting chest pains are caused by anxiety, the body contains many muscles and muscle groups, especially in the chest, rib cage, and diaphragm areas. Muscles respond to nerve impulses. Nerve impulses cause muscles to move by contracting and releasing them. A muscle contracts (tightens) when it receives a nerve impulse, and releases (relaxes) when the nerve impulse stops.
Most of the muscles in the chest, rib cage, and diaphragm are voluntary, meaning we can move them at will. When the body’s nervous system and muscle tensions are normal, the combination of nerve impulses and muscle responses work very well. As a result, the muscles in the chest area function normally.
When the body experiences a stress response[1][2] or is chronically stressed,[3] however, a number of conditions change, including:
- The body’s muscles become tighter (stress hormones cause muscles to tighten).
- The electrical activity in parts of the brain increases.
- The nervous system behaves more involuntarily and erratic.[4]
- The nerves responsible for receiving and reporting information to the brain become more sensitive and reactive (sensitivity and reactivity increase as stress hormone levels rise).
These changes can cause a wide variety of symptoms, including muscles that pulse, throb, twitch, spasm, or contract uncontrollably and involuntarily as the brain sends erratic nerve impulses to the body’s muscles, including those in the chest, ribcage, and diaphragm.
These erratic nerve impulses can cause these muscles to tighten, twitch, spasm, and even ‘lock up.’ These involuntary nerve impulses can also be sent at any time and to any degree. Consequently, a wide variety of contractions from slight to dramatic can occur, which can cause the shooting sharp and stabbing pains in the chest area.
While unsettling and even greatly painful at times, these shooting chest pains symptoms are harmless. They are just an indication of an active stress response and/or stress-response hyperstimulation.
How to get rid of anxiety shooting chest pains?
When anxiety shooting chest pains are caused by apprehensive behavior and the accompanying stress response changes, calming yourself down will bring an end to the stress response and its changes. As your body recovers from the active stress response, these shooting chest pains should subside and you should return to your normal self.
Keep in mind that it can take up to 20 minutes or more for the body to recover from a major stress response. But this is normal and shouldn’t be a cause for concern.
When anxiety shooting chest pains are caused by persistently elevated stress, it may take a lot more time for the body to calm down and recover…and to the point where anxiety- and stress-caused shooting chest pains subside.
As with all anxiety sensations and symptoms, returning your body and nervous system back to their normal, non-hyperstimulated health reduces and eventually eliminates anxiety- and stress-caused sensations and symptoms, including shooting chest pains. But we have to be patient as we faithfully apply our recovery strategies, since recovering from hyperstimulation can take much longer than you might expect. It’s the faithful and diligent application of our recovery strategies that produces results. Recovery is seldom quick.
If the shooting chest pains become too painful, you can talk with your doctor about taking a pain reliever or muscle relaxant to help ease these types of shooting chest pains.
For more information, visit our chest pain anxiety symptoms.
Anxiety Therapy
If you are having difficulty with anxiety, its symptoms, and troublesome worry, you might want to connect with one of our recommended anxiety disorder therapists. Working with an experienced anxiety disorder therapist is the most effective way to overcome problematic anxiety.
All of our recommended therapists have experienced anxiety disorder, have successfully overcome it, and are medication-free. Their years of personal and professional experience make them an excellent choice to work with on your road to recovery.
Common Anxiety Symptoms
The combination of good self-help information and working with an experienced anxiety disorder therapist is the most effective way to address anxiety disorder and its many symptoms. Until the core causes of anxiety are addressed - the underlying factors that motivate apprehensive behavior - a struggle with anxiety disorder can return again and again. Identifying and successfully addressing anxiety's underlying factors is the best way to overcome problematic anxiety.
Additional Resources:
Occasional Quick Sharp Chest Pains
- For a comprehensive list of Anxiety Disorders Symptoms Signs, Types, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment.
- Anxiety and panic attacks symptoms can be powerful experiences. Find out what they are and how to stop them.
- Free online anxiety tests to screen for anxiety. Two minute tests with instant results. Such as:
- Anxiety 101 is a summarized description of anxiety, anxiety disorder, and how to overcome it.
Return to Anxiety Disorder Symptoms section.
anxietycentre.com: Information, support, and therapy for anxiety disorder and its symptoms, including the anxiety shooting chest pains.
Sharp Chest Pain Center
REFERENCES:
1. Selye, H. (1956). The stress of life. New York, NY, US: McGraw-Hill.
2. Folk, Jim and Folk, Marilyn. “The Stress Response And Anxiety Symptoms.” anxietycentre.com, August 2019.
3. Folk, Jim and Folk, Marilyn. 'Stress-response Hyperstimulation.' anxietycentre.com, Nov. 2019.
4. Teixeira, Renata Roland, et al. “Chronic Stress Induces a Hyporeactivity of the Autonomic Nervous System in Response to Acute Mental Stressor and Impairs Cognitive Performance in Business Executives.” Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports., U.S. National Library of Medicine, 2015.
Connect With Us On:
Advertisement
Advertisement
Pain anywhere on the chest is a cause for concern and should always be taken seriously. Two vital organs, namely the heart and lungs, are located in the chest. Therefore pain in the chest may be due to a lung or heart disease which can be deadly. However, chest pain is not always a life threatening symptom. Sometimes even severe chest pain can be due to non-lethal conditions like acid reflux.
Chest Pain Around the Breasts
Identifying the exact location of chest pain is helpful in diagnosing a cause. The type of pain and also other symptoms can also be helpful but sometimes misleading. For example, a burning chest pain is usually associated with chest muscle strain if it is on the surface or with acid reflux (heartburn) if it is felt internally. There are instances where this is not the case and heart attack chest pain can be burning in nature and therefore mistaken for heartburn due to acid reflux.
It is not uncommon to use the breasts as a landmark when assessing chest pain. The pain can be between the breasts (cleavage pain), below the breasts, in or behind the breast and there can be chest pan above the breasts. However, there may be some degree of variation when using the breast as a landmark. This is more likely to be an issue for women due to the significant difference in breast size among individuals.
Organs Above the Breast
On the surface above the breast is the:
- Skin and subcutaneous fat
- Muscles and tendons
- Fascia
- Ligaments
- Ribs
- Clavicle (shoulder bone)
Deeper, within the chest cavity is the:
Occasional Quick Sharp Chest Pain Radiating
- Pleura (lining around the lungs)
- Lungs
The pericardium (lining around the heart), heart and great blood vessels, esophagus (food pipe) and other major structures like the sympathetic trunk like more towards the center of the chest.
Causes of Pain Above Breast
The causes of pain above the breast may be due to a problem of any of the organs and structures mentioned above. We can divided the causes from the chest wall on the surface to the internal organs like the heart and lungs within the chest cavity.
However, it is important to note that the breast itself may be the source of the pain, even if the pain is felt above it. Some of the more likely causes of chest pain above the breast have been discussed in detail below but various other conditions also need to be considered.
Always consult with a medical doctor about chest pain, irrespective of its exact location or nature. Chest pain that occurs with difficulty breathing, dizziness and confusion requires emergency medical attention. One of the most common types of chest pain, heartburn, does not occur with any of these symptoms. Furthermore heartburn is usually central (center of the chest) rather than presenting as side chest pain or pain above the breasts.
Chest Wall
The chest wall if composed of the skin on the surface, fat underneath the skin, connective tissue, muscles, tendons, ligaments, cartilages, joints and bones. Blood vessels and nerves also run in the chest wall.
- Trauma: Injury to the chest wall is one of the leading causes of superficial pain. The pain is usually at the site of the injury. Any trauma, like a blow to the chest above the breast, will therefore be responsible for pain above the breast. Rib and clavicle (collarbone) fractures may be some of the more severe and painful consequences of chest wall injuries.
- Muscle Strain: The pectoral muscles are the largest muscles of the chest wall lying above, behind and below the breasts. This muscle may be strained with overactivity or exertion usually involving certain movements of the arms. This can cause muscle pain around the breast.
- Costochondritis: Inflammation of the joints between the ribs and sternum, including the cartilage between these bones, is known as costochondritis. It typically causes pain at the center of the chest (breastbone pain).
- Shingles: Reactivation of the chickenpox virus can cause inflammation of the skin and underlying tissue, particularly nerves, that may result in painful blisters and skin rash. The chest is commonly affected site and it tends to occur in certain bands (dermatomes).
Read more on chest wall pain.
SYMPTOMS
- Rash, redness, bruising and/or deformity on the chest wall.
- Pain with deep inhalation.
- Pain when moving arms.
- Tenderness of parts of the chest wall.
Breasts
The breasts are technically part of the chest wall. However, there are a variety of breast conditions that may cause chest pain. Normally this pain is in the breast itself but it can also extend to any part above, below or on either side of the breast. These causes can vary from mastitis (infection of the breast), breast cysts, benign tumors of the breast and even breast cancer.
Read more on breast pain.
SYMPTOMS
- Breast secretion or discharge
- Enlarged breast
- Nipple deformity
- Breast rash
- Breast lumps
- Swollen armpit lymph nodes
Lungs
The lungs are the largest organs within the chest cavity. Any disease or disorder of the lungs, particularly when the upper parts of the lungs are involved, can account for chest pain above the breasts. Similarly diseases of the lining around the lungs (pleura) can also be the cause of pain.
- Pleuritis: Also known as pleurisy, this is inflammation of the pleura that surrounds the lungs. It is more likely to occur due to infections or with injury to the pleura that is mostly seen with trauma, such as surgery.
- Bronchitis: Inflammation of the tubes carrying air into and out of the lungs can be responsible for chest pain above the breast. Often this pain may be at the center of the chest but the bronchial tree extends deep into the lungs
- Pneumonia: The lung itself may become inflamed and this is known as pneumonia. Most of the time it is a result of infections, particularly viral or bacterial. This includes conditions like pulmonary TB (tuberculosis). The bronchi may also be involved and this is collectively referred to as bronchopneumonia.
- Chemical pneumonitis: This is inflammation of the lung caused the exposure to certain chemicals. It is more likely to occur with inhaling smoke fumes, pool chlorine, bleachers and drain cleaners as well as pesticides, certain oils and agricultural dusts. Stomach acid may also be responsible as a result of vomit or reflux that enters the lungs (aspiration pneumonia).
- Lung cancer: A malignant tumor of the lung and/or parts of the bronchial tree may also cause chest pain. The pain tends to be the most intense at the part of the lung where the tumor is located. Tobacco smokers and those exposed to second hand smoke are at a greater risk of lung cancer.
SYMPTOMS
- Difficulty breathing
- Abnormal breathing sounds
- Cough
- Sputum (mucus) and bloody phlegm
- Low blood oxygen levels
Heart and Blood Vessels
Although most of the heart is located more centrally whereas the breasts are towards the sides of the chest (lateral), sometimes pain above the breast is due to heart problems or conditions of the great blood vessels.
- Pericarditis: Inflammation of the lining around the heart is known as pericarditis. It can occur with infections or injuries, including surgery to the chest cavity. Sometimes certain medication may also cause pericarditis.
- Carditis: A broad term for inflammation of the heart wall is carditis. This includes inflammation of the muscular layer (myocarditis), inner layer of the heart (endocarditis) as well as the outer layer (pericarditis). The valves may also be inflamed (valvulitis).
- Angina pectoris and heart attack: Both angina pectoris and a heart attack are commonly due to coronary artery disease. The narrowed heart arteries (coronary) arteries can supply sufficient blood to the heart wall and a portion of the tissue may be injured or there may be tissue death.
- Aortic dissection: Tearing of the inner wall of the aorta is known as an aortic dissection. The pain may extend above the breast when the arch of the aorta is affected. It is more likely to occur in older people or where there are pre-existing aortic diseases like an aortic aneurysm.
Read more on cardiac chest pain.
SYMPTOMS
- Shortness of breath
- Lightheaded or dizziness
- Chest pain with/without left arm pain or jaw pain
- Confusion
- Excessive sweating
- Loss of consciousness
Pain Above Right Breast
Pain above the right breast may be due to any of the causes mentioned above but usually does not arise with cardiovascular (heart and blood vessel) conditions. The heart lies in the middle of the chest and slightly to the left. Therefore pain above the right breast is not usually associated with the heart. Sometimes right shoulder pain can be caused by distant problems, like gallstones and other types of gallbladder diseases.
Pain Above Left Breast
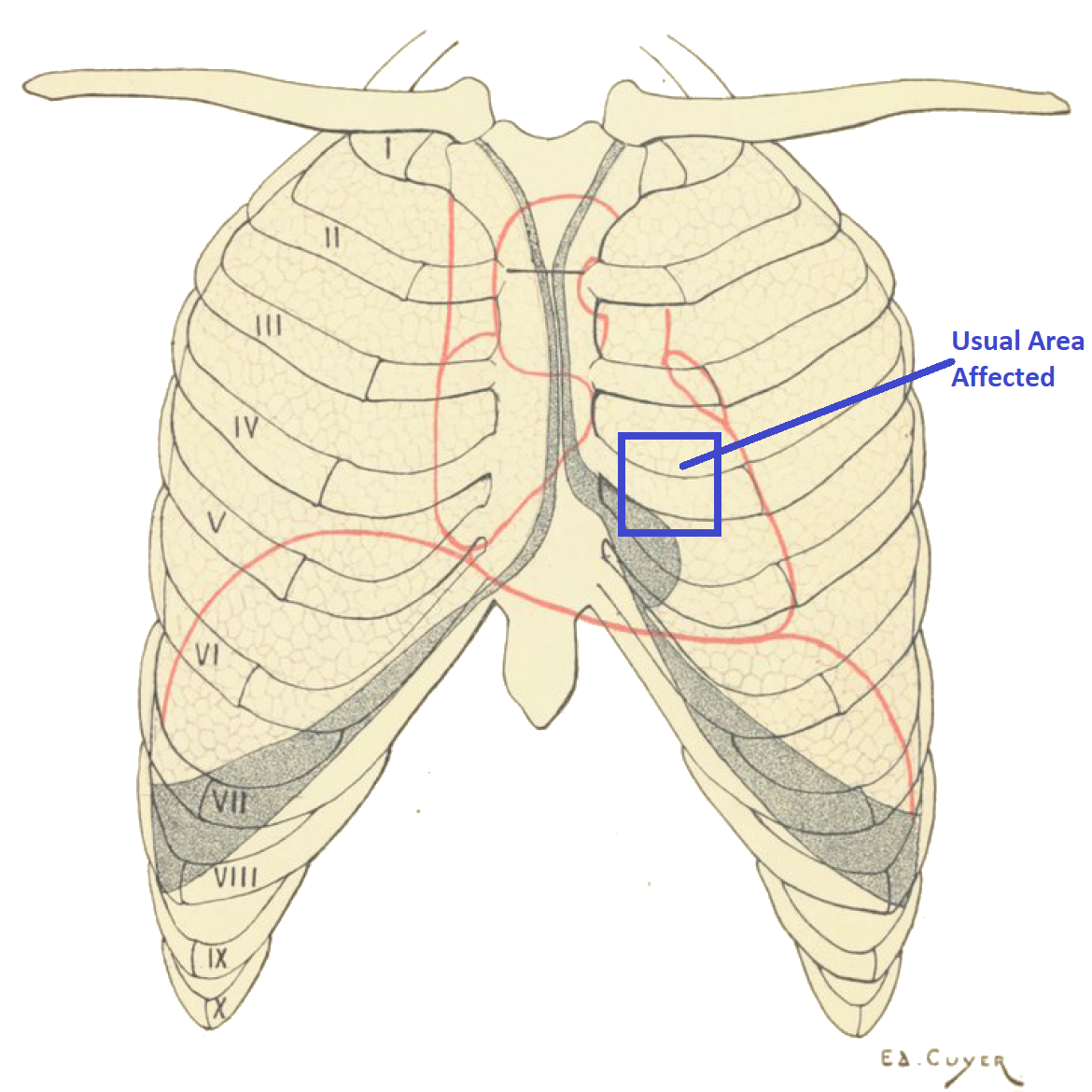
Pain above the left breast may also be caused by any of the conditions mentioned above. Unlike pain above the right breast, a heart or blood vessel problem may also cause pain above the left breast. In fact when pain does occur in thsi region, it is important to rule out the heart as a possible cause particularly people who are at a high risk of a heart attack and other cardiac conditions.
Occasional Quick Sharp Chest Pain
References
- Chest pain. Harvard.edu
- Types of lung diseases. WebMD.com
- Breast pain. MayoClinic.org
Last updated on 28 October 2018.